Iran prepared to deploy troops in Syria
TEHRAN (Basirat): Iran is ready to dispatch troops to Syria, as the case maybe, to monitor compliance with the May 4 agreement with Russia and Turkey to create four “de-escalation zones” in the embattled territory, its Foreign Ministry spokesman said on Monday.
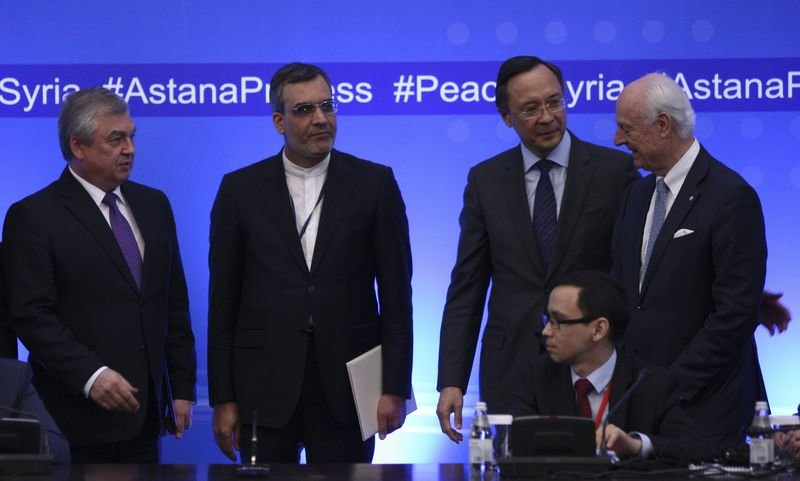

"If necessary conditions are provided, forces have to be dispatched by the three
countries to observe the ceasefire,” Bahram Qassemi told a press conference in
Tehran on Monday.
"If agreed upon, we are prepared to do so.” Similar comments were made by Ali Shamkhani, secretary of Iran's National Security Council and senior coordinator on Syria, days ago.
"If Iran is requested to take more actions (in Syria) such as sending troops to maintain order and security in the de-escalation zones, we are prepared to consider it,” Shamkhani was quoted as having said in an interview with the Russian newspaper Kommersant.
On May 4, Russia, Iran and Turkey signed a document during the fourth round of Syrian talks in Astana, Kazakhstan, to form four "de-escalation zones” in Syria.
The most significant achievement of a three-pronged diplomatic effort since the beginning of 2017 to reduce bloodshed in a war now in its seventh year, the deal brought together three of consequential actors in the conflict from opposite sides.
Russia and Iran back the Syrian government while Turkey supports some of the armed insurgent groups that seek to topple the government.
The top United Nations envoy dealing with Syria, Staffan de Mistura, hailed the memorandum, which took force on May 6, an "important, promising, positive step in the right direction.”
The agreement, which is to last initially for six months, calls for a pause in fighting, including government airstrikes, and for unhindered aid deliveries in and around the four main zones still held by rebels unaffiliated with the Islamic State.
The pact, however, does not apply to militants associated with the Islamic State or a Qaeda-linked group commonly known as the Nusra Front, which were designated as terrorist and hence, left out of the Astana talks.
The de-escalation zones, envisioned as places where displaced Syrian civilians could voluntarily return and settle, include the northern province of Idlib, the central province of Homs, the East Ghouta region outside Damascus, and southern Syria along the Jordanian border.
Neither the Syrian government nor the rebels signed the document although the Syrian government voiced its support for it. Rebel groups objected, arguing it left too many loopholes for the Syrian military to continue what they called indiscriminate bombings of civilian areas.
While the de-escalation zone initiative was implicitly welcome by Washington, which said it supported any effort "genuinely” aimed at creating "a credible, peaceful resolution,” it is unclear how the guarantors will monitor compliance.
Aleksandr Lavrentyev, the Russian negotiator at the talks, told Russian news outlets that Russia could send observers and "work more closely” with countries that back the rebels, including the United States and Saudi Arabia.
In an apparent opposition to the remarks, the Syrian government ruled out the "de-escalation zones” being monitored by other actors, including the United Nations.
"We do not accept a role for the United Nations or international forces to monitor the agreement,” Syrian Foreign Minister Walid al-Moallem was quoted as saying at a news conference in Damascus on May 8.
In addition to the compliance issue, the American intervention in the agreed-upon zones is open to question.
A week ago, American troops attacked Syrian forces, targeting three vehicles that were trying to set up a fighting position on the outskirts of a newly established de-escalation zone close to the Jordanian and Iraqi borders, according to military sources.
Russia, Iran and Turkey have to finalize maps of the de-escalation zones by June 4, though the deadline can be extended.
The fifth round of the Astana talks, set for mid-July, should be different from previous ones as Iraqi forces are close to defeating ISIS militants in Mosul and the surrounding province of Nineveh, which marks the end of the "caliphate” in the country.
There were unconfirmed news that Iraqi Popular Mobilization forces managed to dislodge ISIS fighters from a number of villages west of Mosul, making further progress toward the border with Syria.
Iraq's government is aiming to control the border area with Syria in coordination with the Syrian army.
Linking up the two sides would give President Beshar al-Assad a significant advantage in fighting terrorists in his country.
SOURCE: TehranTimes